Tympanometry Test
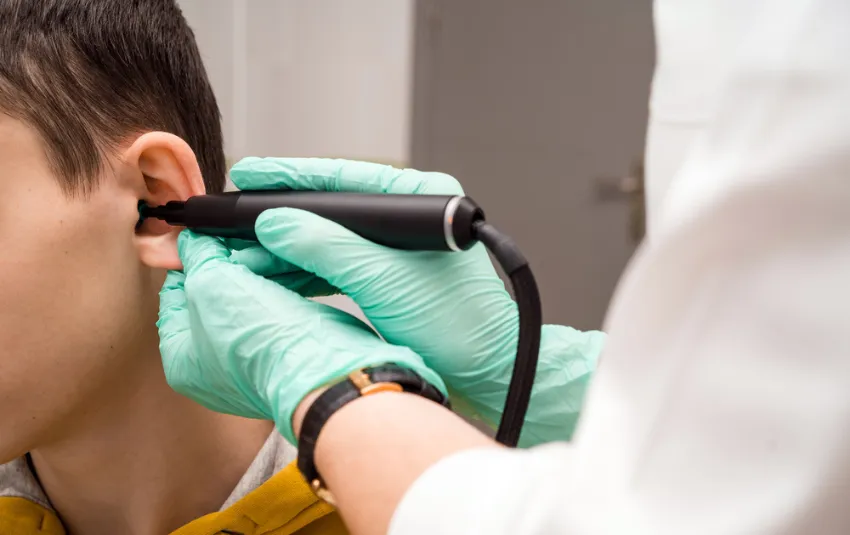
Tympanometry is a diagnostic test used to assess the health and functionality of the middle ear. The middle ear is the space behind the eardrum (tympanic membrane) that contains the three small bones (ossicles) responsible for transmitting sound vibrations from the eardrum to the inner ear. Tympanometry is commonly performed by audiologists and medical professionals to evaluate various aspects of middle ear function.
During a tympanometry test, a small probe is inserted into the ear canal. The probe generates variations in air pressure within the ear canal, which causes the eardrum to move back and forth. The movements of the eardrum are recorded and plotted on a graph, called a tympanogram. This graph provides valuable information about the middle ear’s pressure, compliance (movement), and acoustic impedance.
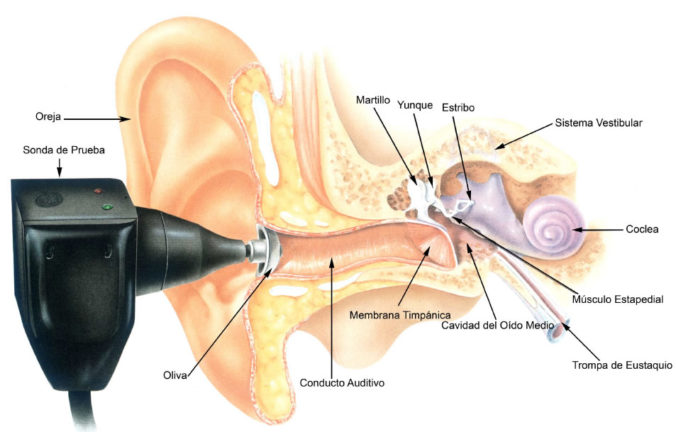
The tympanometry test helps in diagnosing various conditions related to the middle ear, including
Tympanometry can help detect fluid buildup in the middle ear, a common condition in children and adults, which can cause hearing loss and discomfort.
Tympanometry can determine if the eardrum is intact or if there is a perforation.
Accumulation of fluid in the middle ear can be diagnosed using tympanometry.
The Eustachian tubes connect the middle ear to the back of the throat. Dysfunction of these tubes can affect middle ear pressure, and tympanometry can help identify this issue.
This is a condition where the ossicles (middle ear bones) become less mobile due to abnormal bone growth. Tympanometry can provide insights into the stiffness of the eardrum and ossicles.
Abnormal growths or masses in the middle ear can affect the movement of the eardrum, which can be detected through tympanometry.
Tympanometry is a non-invasive and quick test that can provide important information about the health of the middle ear. However, it is often used in conjunction with other tests, such as audiometry, to get a comprehensive understanding of a patient’s hearing health. If you suspect any issues with your ears or hearing, it’s important to consult a medical professional or audiologist for proper evaluation and diagnosis.
